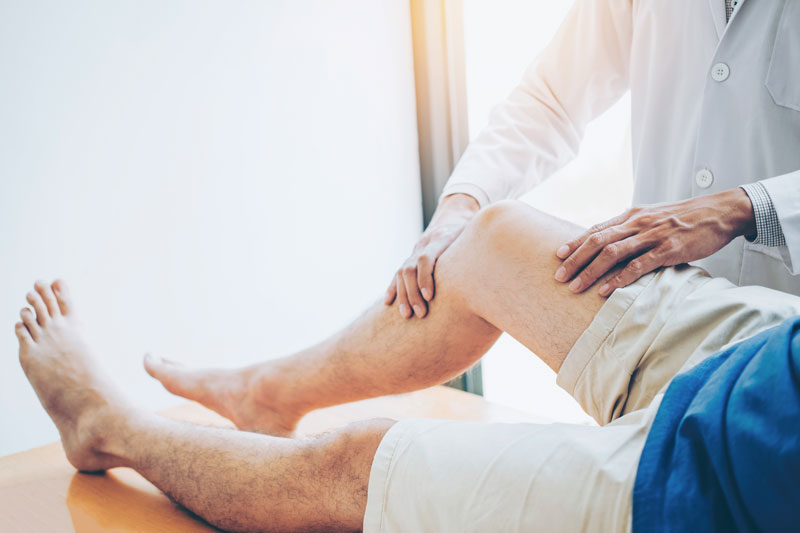
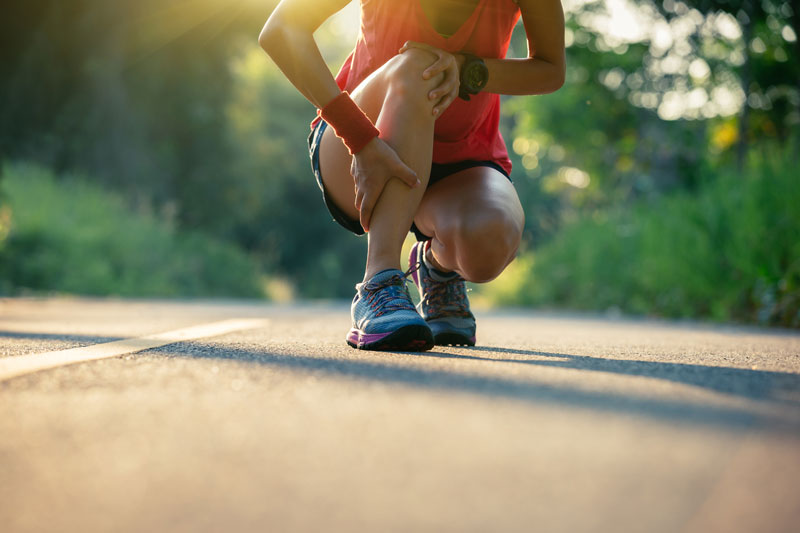
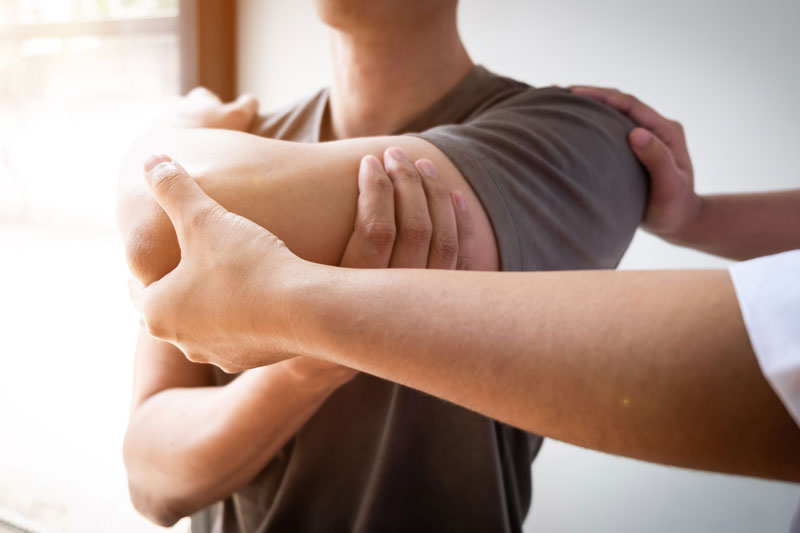
Joint Pain: Joint pain can be debilitating, affecting your mobility and overall quality of life. Whether you’re dealing with arthritis, joint injuries, or other joint-related conditions, our experienced team is here to provide a comprehensive and personal approach. We offer a range of treatment options, including conservative measures such as medical exercise consultations, functional movement analysis, lifestyle modifications, and supplement recommendations. We also specialize in more advanced options like joint injections and other minimally invasive procedures to help with pain. Our goal is to alleviate your joint pain and improve your functionality so that you can enjoy a more active and pain-free life. The most common issues we are treat are:
- Knee Pain
- Shoulder Pain
- Hip Pain
- Elbow Pain
Other Musculoskeletal Pain: Musculoskeletal pain encompasses a wide range of conditions, including muscle strains, ligament injuries, tendonitis, and more. These types of pain can occur almost anywhere in the body, from the head to the feet. Similar to joint pain, we offer a range of treatment options, including conservative measures such as medical exercise consultations, functional movement analysis, lifestyle modifications, and supplement recommendations. We also specialize in more advanced options like nerve, ligament, or tendon injections and other minimally invasive procedures to help with pain. Once again, our goal is to get to the root of the pain so that you can enjoy a more active and pain-free life. The most common musculoskeletal conditions we treat are:
- Bursitis
- Tendonitis
- Muscle strain/pulled muscle
At Ponte Vedra Spine and Pain Center, our mission is to provide compassionate, patient-centered care to our neighbors in Ponte Vedra, Nocatee, and the surrounding areas. We are committed to helping you find relief from joint and musculoskeletal pain so that you can lead a healthier and more active life. Our experienced team utilizes the latest techniques and technologies to ensure you receive the most effective and minimally invasive treatments available. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and take the first step towards a pain-free future.
What is Joint and Musculoskeletal Pain?
Joint pain refers to discomfort or soreness in the joints of the body, where two or more bones meet. It can be caused by various factors, including injury, inflammation, arthritis, or other underlying medical conditions. Joint pain can range from mild to severe and may affect mobility and daily activities.
Musculoskeletal pain encompasses a broader category of discomfort that includes not only joint pain but also pain in muscles, tendons, ligaments, and other structures that support the musculoskeletal system. Musculoskeletal pain can result from overuse, strain, injury, inflammation, or underlying medical conditions like fibromyalgia. It can manifest as localized or widespread pain and can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and physical function.

What Causes Joint and Musculoskeletal Pain?
Joint and musculoskeletal pain can be caused by various factors, including:
1. Injury:
Acute injuries, such as sprains, strains, fractures, or dislocations, can lead to joint and musculoskeletal pain.
2. Inflammation:
Inflammatory conditions like arthritis (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis) can cause chronic joint pain. Other inflammatory disorders like tendinitis or bursitis can affect the musculoskeletal system.
3. Overuse or Repetitive Strain:
Repeated motions or overuse of muscles and joints, often seen in activities or jobs that involve repetitive movements, can lead to pain and discomfort.
Infections: Certain infections, like Lyme disease or viral illnesses, can cause joint and muscle pain as part of their symptoms.
4. Autoimmune Disorders:
Conditions like lupus or ankylosing spondylitis involve the immune system attacking the body’s own tissues, which can result in joint and musculoskeletal pain.
5. Degenerative Changes:
Age-related wear and tear on joints and tissues can lead to conditions like osteoarthritis, which causes pain and reduced joint function.
6. Metabolic Disorders:
Conditions like gout, which result from the buildup of uric acid crystals in joints, can cause severe joint pain.
It’s important to note that the specific cause of joint and musculoskeletal pain can vary widely from person to person. Accurate diagnosis by a healthcare professional is crucial to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
What are the symptoms of Joint and Spine Pain?
The symptoms of joint and musculoskeletal pain can vary depending on the underlying cause and the specific structures affected. However, some common symptoms include:
Joint Pain:
- Pain: The primary symptom is discomfort or pain in the affected joint(s). The pain can range from mild to severe and may be constant or intermittent.
- Swelling: Inflammation of the joint can lead to swelling, which may make the joint appear larger or feel warm to the touch.
- Stiffness: Joint stiffness can make it difficult to move the affected joint, particularly after periods of inactivity or in the morning.
- Redness and warmth: Inflammation in the joint can cause redness and an increase in skin temperature over the affected area.
- Limited range of motion: Pain and stiffness can restrict the joint’s ability to move fully, leading to a decreased range of motion.
Musculoskeletal Pain:
- Pain: Musculoskeletal pain can be localized to a specific muscle or area or may be more diffuse, affecting multiple areas of the body. The pain can be sharp, dull, aching, or throbbing.
- Muscle spasms: Some individuals with musculoskeletal pain may experience muscle spasms or involuntary contractions.
- Tenderness: The affected muscles, tendons, or ligaments may feel tender to the touch.
- Fatigue: Chronic musculoskeletal pain can lead to fatigue and a feeling of overall weakness.
- Decreased function: Depending on the severity of the pain, individuals may experience a decrease in their ability to perform daily activities and tasks.
What are the Treatment Options for Joint and Musculoskeletal Pain?
The treatment options for joint pain can vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the pain. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and to discuss the most appropriate treatment plan. Here are some common treatment options for joint pain:
1. Lifestyle and Self-Care:
- Rest: Avoid overusing the affected joint and give it time to heal.
- Ice and Heat: Applying ice packs and/or warm compresses can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can alleviate stress on the joints, especially for weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips.
- Exercise: Low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, can help improve joint flexibility and strength. It is important to focus on the supporting muscles, tendons, and ligaments of the painful area. Providing balanced support to the area in question can help support it over the longer term.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can create a tailored exercise program to improve joint function.
2. Joint Injections:
- Hyaluronic Acid Injections: These injections can provide lubrication and cushioning to the joint, particularly for osteoarthritis.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) or Bone Marrow Concentrate Therapy: Injections use a concentrated form of the patient’s own blood or bone marrow to promote healing in damaged joints.
- Nerve blocks: Oftentimes blocking the nerve that goes to the painful area can help relieve symptoms while healing can occur.
3. Alternative Therapies:
- Acupuncture: Some people find relief from joint pain through acupuncture.
- Chiropractic Care: Spinal adjustments and manipulations may alleviate joint pain, particularly in the back and neck.
- Supplements: Some individuals can find relief through various anti-inflammatory supplements including turmeric, omega 3 fatty acids, Boswellia, and others.
4. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Dietary Changes: A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods (e.g., fruits, vegetables, fatty fish) may help reduce joint pain.
- Stress Reduction: Stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help improve overall well-being and potentially reduce joint pain.
5. Assistive Devices:
- Joint Braces or Splints: These devices can provide support and stability to the affected joint. However, it is important to not become reliant on these devices.
- Canes, Crutches, or Walkers: These assistive devices can help reduce the load on the joints when walking, giving time for the affected area to heal.
6. Medications:
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Prescription Medications: In some cases, stronger prescription NSAIDs or other medications may be necessary.
- Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory drugs may be injected directly into the affected joint to reduce inflammation and pain.
7. Surgery:
- Occasionally when more conservative measures have failed and the problem is severe, surgery can be considered.
It’s crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment approach for your specific joint pain condition. They can tailor a treatment plan to address the underlying cause, manage pain, and improve your joint function and quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions about Joint and Musculoskeletal Pain
Here is a list of frequently asked questions (FAQs) about other pain conditions, along with brief answers to each question:
1. What are the most common types of arthritis that cause joint pain?
Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are the most common types of arthritis that lead to joint pain. Osteoarthritis is often age-related, while rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease.
2. When should I see a doctor for joint pain?
You should see a doctor if your joint pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms like swelling, redness, or loss of joint function.
3. How is joint pain diagnosed?
Some pain issues can be diagnosed with a thorough physical examination and medical history review. Other times diagnostic imaging tests (X-rays, MRIs), and sometimes blood tests to identify underlying causes.
4. Can joint pain be managed without medication?
Yes, lifestyle changes, physical therapy, exercise, weight management, and assistive devices can often help manage joint pain without medication.
5. What medications are commonly used to treat joint pain?
Over-the-counter NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen), prescription NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and pain relievers can all be options used to manage joint pain. However, these are best used for the short term while other treatment options are undertaken.
6. Are there non-surgical treatments for joint pain?
Yes, non-surgical treatments include physical therapy, joint injections and lifestyle modifications.