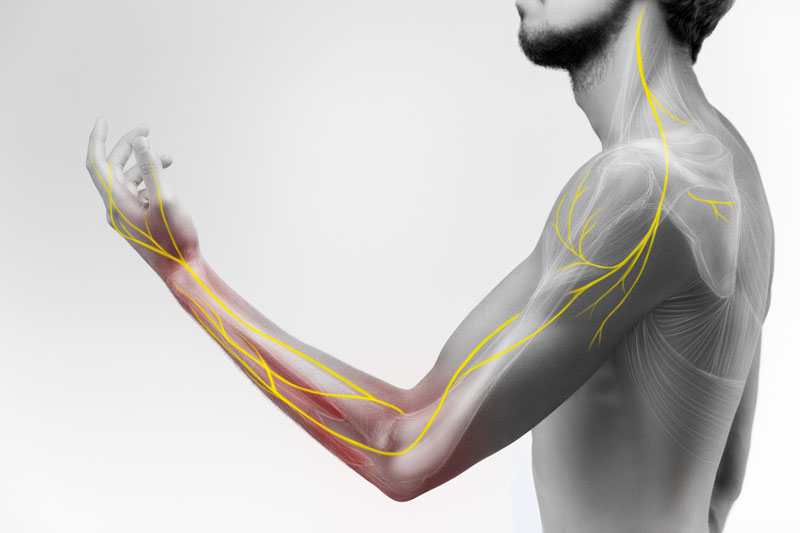
Nerve Pain: Nerve pain can be another type of devastating pain affecting various parts of the body, most commonly the arms and legs. Whether you have arm or leg symptoms related to nerve pain, we are here to provide comprehensive care. There are a range of treatment options for nerve pain, including conservative measures such as physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle modifications, as well as advanced interventions like nerve blocks, ablations, hydrodissections, or other minimally invasive procedures when needed. Our goal is to alleviate your nerve pain which will allow you to function better so that you can enjoy a more active and pain-free life.
At Ponte Vedra Spine and Pain Center, our mission is to provide compassionate, patient-centered care to residents in Ponte Vedra, Nocatee, and the surrounding areas. We are committed to helping you find relief from nerve pain so that you can lead a healthier and more active life. Our experienced team utilizes the latest techniques and technologies to ensure you receive the most effective and minimally invasive treatments available. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and take the first step towards a pain-free future.
What is Nerve Pain?
Nerve pain, also known as neuropathic pain, is a type of pain that results from abnormalities or damage to the nerves in the peripheral or central nervous system. Unlike typical pain sensations that come from other joint or soft tissue injuries, nerve pain is often characterized by abnormal and distressing sensations, including burning, shooting, stabbing, tingling, or electric shock-like feelings. It can be persistent and debilitating, significantly affecting a person’s quality of life.
Nerve pain can have various underlying causes, such as diabetes, nerve compression (e.g., from herniated discs), infections (e.g., shingles), autoimmune diseases (e.g., multiple sclerosis), chemotherapy-related nerve damage (chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy), and certain medications. In some cases, the exact cause of nerve pain remains unknown (idiopathic neuropathy).
Managing nerve pain can be challenging, and treatment approaches often involve a combination of medications, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, and, in some cases, minimally invasive procedures or surgeries. The goal of treatment is to alleviate the pain, improve function, and enhance your overall quality of life.
Effective management of nerve pain typically requires a personalized and multidisciplinary approach, and we can tailor treatments to the specific underlying cause and the patient’s individual needs. It’s essential for patients experiencing nerve pain to seek medical evaluation and guidance to address this often chronic and distressing condition.

What Causes Nerve Pain?
Nerve pain can be caused by various factors and conditions that affect the peripheral or central nervous system. The specific causes of nerve pain can vary, but they generally fall into the following categories:
1. Nerve Damage or Injury: Nerve pain often results from damage or injury to nerves. This can occur due to:
- Trauma or physical injuries, such as accidents or falls.
- Compression or pressure on nerves, which can be caused by conditions like herniated discs or carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Surgical procedures that involve nerve manipulation or damage.
- Radiation therapy, which can damage nerves in the treatment area.
2. Medical Conditions: Several medical conditions can lead to nerve pain, including:
- Diabetes: Diabetic neuropathy is a common cause of nerve pain, resulting from high blood sugar levels damaging nerves over time.
- Infections: Certain infections like herpes zoster (shingles), HIV, and Lyme disease can affect nerves and cause neuropathic pain.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis can lead to nerve damage and subsequent pain.
- Kidney Disease: Nerve pain can be a complication of advanced kidney disease.
- Alcohol Use: chronic use of alcohol is also associated with neuropathic pain.
- Chemotherapy and Medications: Some medications, especially certain chemotherapy drugs and antiretroviral drugs used in HIV treatment, can cause neuropathy and nerve pain as side effects.
4. Toxic Exposures: Exposure to toxins and chemicals, such as heavy metals, can damage nerves and result in neuropathic pain.
5. Idiopathic Neuropathy: In some cases, the exact cause of nerve pain remains unknown. This is referred to as idiopathic neuropathy.
6. Genetic Factors: Rarely, genetic factors can predispose individuals to nerve disorders that cause chronic pain.
Nerve pain can manifest as various sensations, including burning, stabbing, tingling, electric shock-like sensations, or numbness. It’s essential for individuals experiencing persistent nerve pain to seek medical evaluation and care to determine the cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
What are the Symptoms of Nerve Pain?
Nerve pain or inflammation can manifest with a variety of symptoms that are often described as abnormal or unusual sensations. These symptoms can vary in intensity and may include:
1. Burning Sensation: Many individuals with nerve pain experience a persistent burning sensation in the affected area. This sensation can range from mild discomfort to severe and excruciating pain.
2. Shooting or Electric Shock-Like Pain: Nerve pain may cause sudden, shooting, or electric shock-like pains that come and go in short bursts. These pains can be intense and unpredictable.
3. Tingling or Pins and Needles: Some people describe nerve pain as a continuous sensation of tingling, pins and needles, or prickling in the affected area.
4. Numbness: Nerve damage can lead to numbness or loss of sensation in the affected area. This can make it difficult to feel touch, temperature changes, or pressure.
5. Stabbing or Stinging Sensations: Nerve pain may be experienced as sharp, stabbing, or stinging sensations that can be triggered by touch or movement.
6. Throbbing: Nerve pain can also manifest as a throbbing or pulsating sensation, similar to a heartbeat, in the affected area.
7. Increased Sensitivity: Some individuals with nerve pain become hypersensitive to stimuli, experiencing heightened pain with even light touch or temperature changes.
8. Muscle Weakness: In some cases, nerve damage can lead to muscle weakness or difficulty controlling and coordinating movements in the affected area.
9. Itching: Itching, often intense and persistent, can be a symptom of nerve pain, especially in conditions like neuropathic itch.
The specific symptoms of nerve pain can vary depending on the underlying cause and location of the nerve damage. Nerve pain can affect any part of the body and may be localized to a specific area or radiate along a nerve pathway.
What are the Treatment Options for Nerve Pain?
The treatment of nerve pain can be challenging and often requires a multidimensional approach tailored to the underlying cause and the individual’s specific symptoms. Here are various treatment options commonly used to manage nerve pain:
1. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Avoiding activities or positions that exacerbate pain.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and stress management.
2. Physical Therapy:
- Physical therapy can help improve muscle strength and flexibility, correct posture, and reduce the pressure on affected nerves.
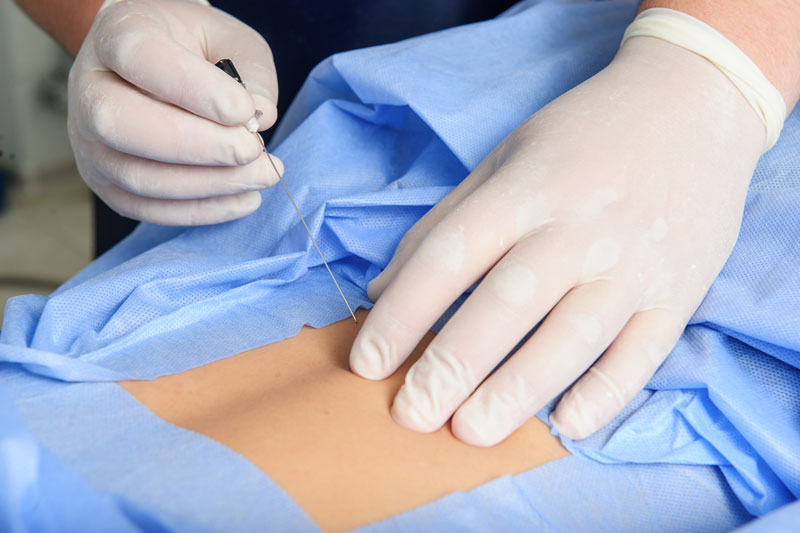
3. Nerve Blocks and Injections:
- Nerve blocks or injections with local anesthetics or steroids can provide temporary relief by numbing or reducing inflammation around the affected nerve.
4. Medications:
- Anticonvulsants: Drugs like gabapentin and pregabalin are often prescribed to reduce nerve-related pain by stabilizing overactive nerve cells.
- Tricyclic Antidepressants: Medications like amitriptyline can help alleviate nerve pain, even in individuals who are not depressed.
- Selective Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs): Drugs like duloxetine can provide pain relief and improve mood in some cases.
- Topical Medications: Creams or patches containing lidocaine or capsaicin can be applied directly to the painful area for localized relief.
5. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS):
- TENS units deliver electrical impulses through the skin to stimulate nerves and provide pain relief.
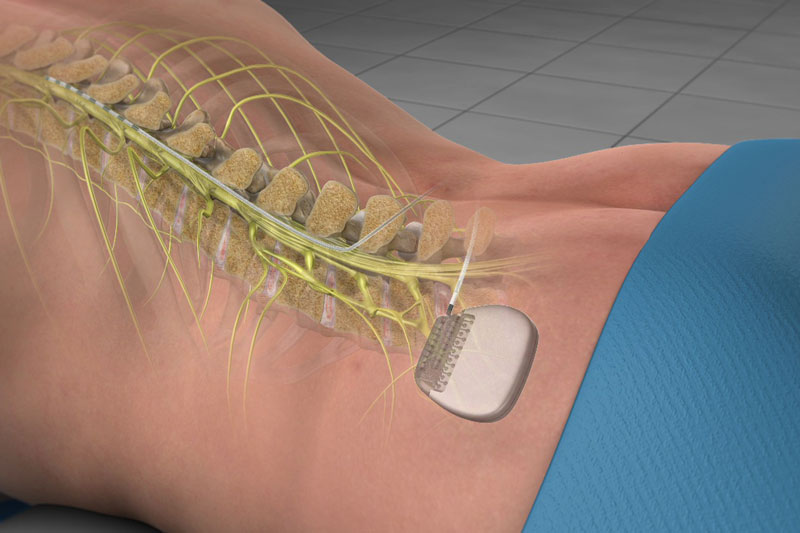
6. Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS):
- SCS involves implanting a device that delivers electrical impulses to the spinal cord, disrupting pain signals and reducing pain perception.
7. Complementary Therapies:
- Acupuncture, massage therapy, and relaxation techniques can sometimes provide relief from nerve pain.
8. Surgery:
- In severe cases, surgical interventions like nerve decompression, nerve repair, or even amputation (as a last resort) may be considered.
9. Management of Underlying Conditions:
- Addressing and managing the underlying medical conditions contributing to nerve pain, such as diabetes or autoimmune diseases.
The choice of treatment depends on the individual’s specific symptoms, the underlying cause of the nerve pain, and the overall health of the patient. It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare provider or pain specialist to develop a personalized treatment plan that effectively manages nerve pain while minimizing side effects and addressing the root cause when possible.
Frequently Asked Questions About Nerve Pain
Here is a list of frequently asked questions (FAQs) about nerve pain, along with brief answers to each question:
1. What is nerve pain, or neuropathic pain?
- Nerve pain, also known as neuropathic pain, is a type of chronic pain that results from abnormalities or damage to the nerves in the peripheral or central nervous system.
2. What are the common causes of nerve pain?
- Nerve pain can be caused by various factors, including nerve damage or injury, medical conditions (such as diabetes and multiple sclerosis), infections, toxic exposures, and certain medications.
3. What are the typical symptoms of nerve pain?
- Symptoms of nerve pain may include burning sensations, shooting or electric shock-like pains, tingling or pins and needles, numbness, stabbing sensations, and muscle weakness.
4. When should I seek medical attention for nerve pain?
- You should seek medical help if you experience persistent or worsening nerve pain, especially if it interferes with your daily life or is associated with other concerning symptoms such as weakness.
5. How is nerve pain diagnosed?
- Diagnosis often involves a medical history review, physical examination, and sometimes imaging studies or nerve function tests to determine the underlying cause.
6. What are the available treatments for nerve pain?
- Treatment options may include medications (anticonvulsants, antidepressants), physical therapy, nerve blocks, topical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and, in some cases, surgical interventions.
7. Are there any lifestyle changes that can help manage nerve pain?
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, balanced nutrition, stress management, and avoiding activities that worsen symptoms, can aid in managing nerve pain.
8. Can nerve pain be cured completely?
- Nerve pain is often a chronic condition, but effective management can significantly reduce symptoms and improve quality of life in many cases.
9. Are there alternative therapies or complementary treatments for nerve pain?
- Complementary therapies like acupuncture, massage therapy, and relaxation techniques may provide relief for some individuals with nerve pain.
10. What is the role of medications in treating nerve pain?
- Medications, such as anticonvulsants, antidepressants, and pain relievers, are commonly used to manage nerve pain by altering pain perception and nerve function.
11. What are the potential side effects of medications used for nerve pain?
- Side effects can vary depending on the medication, but common side effects may include dizziness, drowsiness, weight gain, or changes in mood.
12. Can nerve pain be prevented?
- Preventing nerve pain often involves managing underlying medical conditions, avoiding toxic exposures, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
13. What should I discuss with my healthcare provider when seeking treatment for nerve pain?
- It’s essential to discuss your symptoms, medical history, current medications, and any concerns or questions you have about treatment options with your healthcare provider.
14. Are there support groups or resources available for individuals with nerve pain?
- Yes, support groups and online resources can provide valuable information and emotional support for individuals living with nerve pain.
Remember that nerve pain is a complex condition, and the effectiveness of treatment can vary among individuals.