Spine conditions such as neck pain and low back pain can be debilitating, affecting your mobility and overall quality of life. Whether you’re dealing with arthritis, herniated discs, sciatica, or other spine related conditions, our experienced team of healthcare professionals is here to provide comprehensive care. We offer a range of treatment options, including conservative measures such as physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle modifications, as well as advanced interventions like injections and minimally invasive procedures. Our goal is to alleviate your neck and back pain and improve your functionality so that you can enjoy a more active and pain-free life.
At Ponte Vedra Spine and Pain, our mission is to provide compassionate, patient-centered care to residents in Ponte Vedra and the surrounding areas. We are committed to helping you find relief from Joint and Musculoskeletal Pain so that you can lead a healthier and more active life. Our experienced team utilizes the latest techniques and technologies to ensure you receive the most effective and minimally invasive treatments available. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and take the first step towards a pain-free future.
What are Spine Conditions?
Spine conditions refer to a wide range of medical conditions and disorders that affect the spine, which is the central bony structure in the human body that provides support and protection for the spinal cord and facilitates various movements. These conditions can affect the bones, discs, nerves, muscles, and ligaments of the spine and may result in a variety of symptoms and limitations. Some common spine conditions include:
1. Herniated Discs: When the soft inner core of a spinal disc pushes through its tough outer shell, it can compress nearby nerves, causing pain, numbness, and weakness. This condition is also known as a slipped or ruptured disc.
2. Degenerative Disc Disease: Over time, the discs in the spine can degenerate, leading to a decrease in disc height and function. This condition can cause pain and reduced mobility.
3. Spinal Stenosis: This is the narrowing of the spaces within the spine, often compressing the spinal cord and nerves. It can result in pain, numbness, and weakness, typically in the lower back and legs (lumbar stenosis) or neck and arms (cervical stenosis).
4. Scoliosis: Scoliosis is an abnormal curvature of the spine, often in a lateral or sideways direction. It can be congenital (present at birth) or develop during growth, leading to spinal deformity and potential complications.
5. Kyphosis: Kyphosis is an excessive forward rounding of the upper spine, resulting in a hunched or “humpbacked” appearance. It can cause back pain and affect posture and mobility.
6. Spondylolisthesis: This condition occurs when one vertebra slips forward over an adjacent vertebra. It can lead to pain, nerve compression, and instability of the spine.
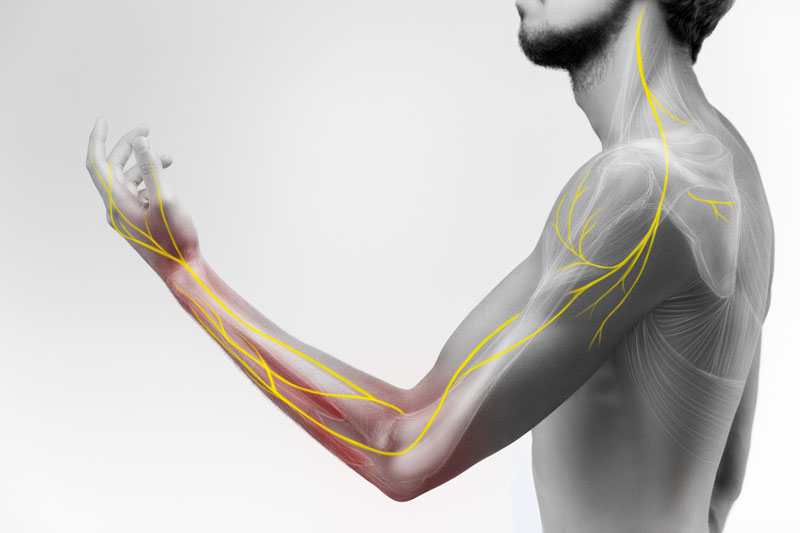
7. Radiculopathy (Sciatica): This condition involves the compression or irritation of spinal nerves, often leading to radiating pain, tingling, or weakness along the nerve’s pathway.
Treatment for spine conditions depends on the specific diagnosis and may include conservative approaches like physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle modifications, or more invasive interventions such as surgery. The goal of treatment is typically to alleviate pain, improve function, and enhance the patient’s quality of life. Spine conditions should be evaluated and managed by healthcare professionals, often with the expertise of orthopedic surgeons or neurosurgeons specializing in spine disorders.
What Causes These Spine Conditions?
These spine conditions can have various causes, and they often result from a combination of factors. These factors may be related to age, lifestyle, genetics, injuries, or underlying medical conditions. Here are some common causes of spine conditions:
1. Aging: As people age, the spine undergoes natural wear and tear, which can lead to degenerative changes in the spinal discs, joints, and bones. This is a common cause of conditions like degenerative disc disease and osteoarthritis.
2. Genetics: Some spine conditions have a hereditary component. If you have a family history of conditions like scoliosis or ankylosing spondylitis, you may be at an increased risk.
3. Trauma: Accidents, falls, and injuries can damage the spine’s structures, leading to conditions like spinal fractures, herniated discs, and spinal cord injuries.
4. Poor Posture: Consistently maintaining poor posture, especially when sitting or standing for long periods, can place excessive stress on the spine, potentially causing conditions like excess kyphosis or lordosis.
5. Obesity: Excess body weight places increased pressure on the spine, especially in the lumbar (lower back) region. This can contribute to conditions like herniated discs and spinal stenosis.
6. Repetitive Strain: Certain occupations or activities that involve repetitive movements or heavy lifting can strain the spine over time, increasing the risk of conditions like spondylolisthesis or muscle and ligament strains.
7. Infections: In rare cases, infections of the spine or nearby structures can lead to conditions like spinal abscesses or vertebral osteomyelitis.
8. Inflammatory Disorders: Conditions like ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, and other autoimmune disorders can cause chronic inflammation in the spine, leading to pain and stiffness.
9. Metabolic Conditions: Metabolic disorders like osteoporosis can weaken the bones of the spine, making them more susceptible to fractures and compression fractures.
10. Poor Physical Fitness: Lack of regular physical activity and weak core muscles can contribute to spine conditions by failing to support and stabilize the spine effectively.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, practicing good posture, engaging in regular exercise, and taking precautions to avoid injuries can reduce the risk of developing certain spine conditions and promote overall spinal health. If you experience persistent back or neck pain or have concerns about your spine health, speak with us today.
What are the Symptoms of These Spine Conditions?
The symptoms of these spine conditions can vary widely depending on the specific condition and its severity. While each spine condition may present its own set of symptoms, some common symptoms associated with various spine conditions include:
1. Back or Neck Pain: Persistent pain in the back (lumbar region) or neck (cervical region) is a common symptom of many spine conditions. The pain may be dull, aching, sharp, or radiating.
2. Radiating Pain: Pain that radiates from the spine into other areas of the body, such as the legs (sciatica) or arms, is a characteristic symptom of conditions like herniated discs or spinal stenosis.
3. Numbness and Tingling: A feeling of numbness, tingling, or pins and needles sensation in the arms, hands, legs, or feet may occur when spinal nerves are compressed or irritated.
4. Muscle Weakness: Weakness in the arms or legs may be experienced, particularly when spinal nerves are affected. This can result in difficulty with lifting objects, walking, or performing daily activities.
5. Limited Range of Motion: Conditions like spinal arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis can cause stiffness and a reduced range of motion in the spine, making it difficult to bend, twist, or move freely.
6. Changes in Posture: Spine conditions like scoliosis can lead to changes in posture, causing the spine to curve abnormally. This may result in uneven shoulders or hips and an altered appearance.
7. Balance and Coordination Problems: Spinal cord compression or injuries can affect balance and coordination, leading to issues with walking and fine motor skills.
8. Leg or Arm Pain: Conditions like radiculopathy (pinched nerve) can cause localized pain and discomfort in the arms or legs.
9. Sciatica: Sciatica is characterized by pain that radiates down the back of the leg. It is often caused by compression of the sciatic nerve, typically due to a herniated disc.
10. Spinal Deformities: Conditions like kyphosis (excessive forward rounding of the upper spine) or lordosis (inward curvature of the lower spine) may lead to visible changes in posture.
11. Fracture Symptoms: Spinal fractures can cause severe pain, especially with movement or pressure on the spine. Vertebral compression fractures may result in a loss of height.
12. Systemic Symptoms: Some spine conditions, especially those involving inflammation, may lead to systemic symptoms such as fatigue, fever, and weight loss.
It’s important to note that the severity of symptoms can vary, and some individuals with spine conditions may experience only mild discomfort, while others may have significant pain and functional limitations. Additionally, some spine conditions may be asymptomatic until they progress to an advanced stage. If you experience persistent or worsening symptoms related to your spine, it’s essential to speak with us today. Early intervention can often lead to better outcomes and improved quality of life.
What are the Treatment Options for These Spine Conditions?
Treatment options for these spine conditions depend on the specific diagnosis, the severity of symptoms, the patient’s overall health, and other individual factors. Here are some common treatment options for various spine conditions:
1. Lifestyle and Self-Care:
- Exercise and Physical Activity: Regular exercise can help strengthen the muscles that support the spine and improve overall spine health.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce stress on the spine and decrease the risk of certain spine conditions.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking can improve blood flow to the spine and reduce the risk of complications during spine surgery.
- Posture and Ergonomics: Practicing good posture and making ergonomic adjustments in the workplace can reduce strain on the spine.
2. Conservative Treatments:
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve posture, strength, flexibility, and overall spine health. Therapists provide exercises and techniques to alleviate pain and improve function.
- Medications: Pain-relieving medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, or analgesics, may be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold packs can help reduce pain and inflammation in the affected area.
- Activity Modification: Lifestyle changes, including ergonomic adjustments at work or home, can reduce stress on the spine.
3. Interventional Procedures:
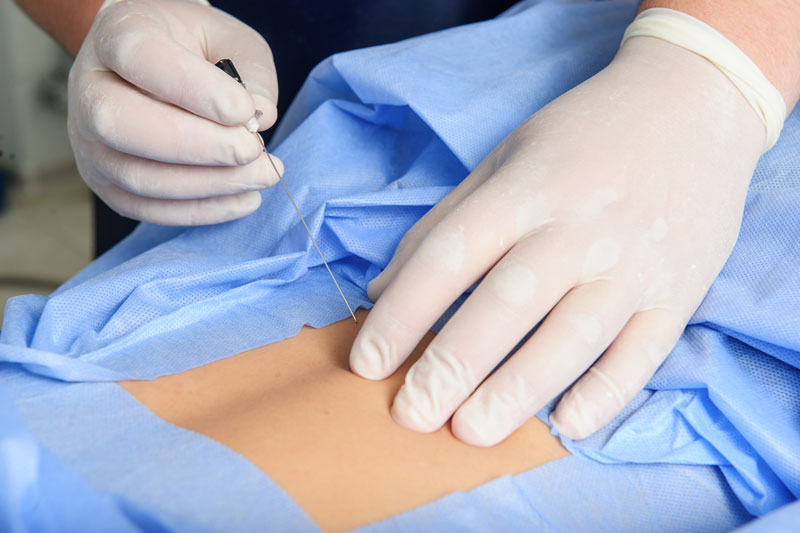
- Epidural Steroid Injections: These injections can provide relief for conditions causing nerve compression or inflammation, such as herniated discs or spinal stenosis.
- Facet Joint Injections: Facet joints injections can alleviate pain and inflammation in the spinal joints.
- Radiofrequency Ablation: This procedure uses heat to disrupt nerve signals in the spine, providing relief for chronic back pain.
- Nerve Blocks: Nerve blocks involve the injection of anesthetic or anti-inflammatory medication to block pain signals from specific nerves.
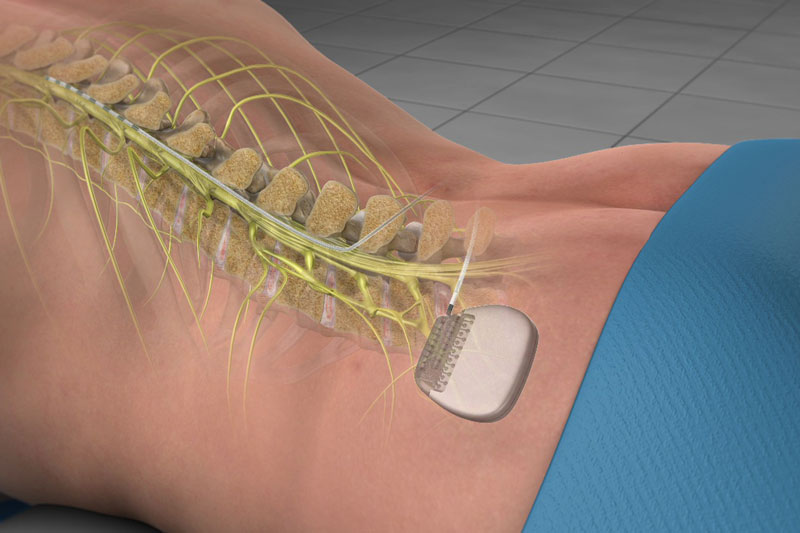
- Spinal Cord Stimulation: In cases of chronic pain that does not respond to other treatments, a spinal cord stimulator may be implanted to manage pain.
4. Medication Management:
- Neuropathic Medications: Medications like gabapentin or pregabalin can help manage neuropathic pain associated with nerve compression or injury.
- Disease-Modifying Medications: For conditions like ankylosing spondylitis, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and slow disease progression.
5. Surgery:
- Spinal Fusion: Spinal fusion surgery may be recommended to stabilize the spine and relieve pain in cases of severe degenerative disc disease, spondylolisthesis, or spinal fractures.
- Discectomy: This procedure involves the removal of a herniated disc to relieve nerve compression.
- Laminectomy: A laminectomy can be performed to create more space in the spinal canal and alleviate pressure on the spinal cord and nerves, commonly used for spinal stenosis.
- Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty: These procedures are used to treat vertebral compression fractures by stabilizing and reinforcing the affected vertebrae.
- Scoliosis Surgery: Surgical correction of scoliosis may be recommended for severe cases, involving the placement of spinal instrumentation and fusion.
Treatment plans are individualized to each patient’s needs and may involve a combination of these options. The choice of treatment is made collaboratively with the patient with the goal of reducing pain, improving function, and enhancing the patient’s quality of life. Early intervention and conservative treatments are often preferred before considering more surgery.
Frequently Asked Questions About These Spine Conditions
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about these spine conditions and their answers:
1. What are common symptoms of these spine conditions?
- Common symptoms include back or neck pain, radiating pain into the arms or legs, numbness, tingling, muscle weakness, changes in posture, and limited range of motion.
- What causes these spine conditions?
- Spine conditions can be caused by a variety of factors, including aging, genetics, trauma, poor posture, obesity, infections, inflammatory disorders, and metabolic conditions like osteoporosis.
2. Can these spine conditions be prevented?
- While some spine conditions are not preventable, adopting a healthy lifestyle, maintaining good posture, staying physically active, and avoiding excessive strain on the spine can help reduce the risk of certain conditions.
3. How are these spine conditions diagnosed?
- Spine conditions are typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examinations, imaging studies (X-rays, MRI, CT scans), and sometimes specialized tests like electromyography (EMG).
4. What are conservative treatments for these spine conditions?
- Conservative treatments include physical therapy, medications, heat/cold therapy, lifestyle modifications, bracing, and rest. These approaches aim to alleviate pain and improve function without surgery.
5. When is surgery recommended for these spine conditions?
- Surgery is considered when conservative treatments do not provide relief, or when a spine condition poses a risk to the patient’s health or mobility. It may be recommended for conditions like severe herniated discs, spinal fractures, or spinal instability.
6. Is physical therapy effective for these spine conditions?
- Physical therapy is often effective in improving spine conditions. It can help reduce pain, strengthen supporting muscles, enhance flexibility, and improve overall spine health.
7. Is surgery the only option for severe spine conditions?
- Surgery is not always the first or only option for severe spine conditions. Many patients find relief through conservative treatments or interventional procedures. Surgery is typically considered when other treatments are ineffective or when there’s a risk of neurological damage.
8. Can lifestyle changes help manage these spine conditions?
- Yes, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, proper ergonomics, and smoking cessation can help manage and improve the outcomes of many spine conditions.
It’s important to note that the specific diagnosis and treatment plan for spine conditions vary from person to person. Patients are encouraged to consult with us to receive a thorough evaluation and personalized guidance based on their unique circumstances.